Isaura Beatriz Borges Silva
Advisor: Profa. Dra. Mari Cleide Sogayar
Collaborating researches: Ana Cláudia Oliveira Carreira; Milton Yutaka Nishiyama Junior; Fernando Janczur Velloso; Fernando Henrique Lojudice; Camila Harumi Kimura.
Graduated in biotechnology from the Federal University of Uberlândia (2017). Master’s degree in biotechnology from the Institute of Biomedical Sciences at the University of São Paulo (2019). Currently a doctoral student in biochemistry at the Institute of Chemistry of the University of São Paulo. Develops a doctoral project entitled: ‘‘Characterization of embryonic stem cell transcriptome during its differentiation into insulin-producing cells in the absence and presence of peptide growth/differentiation factors” at the NUCEL group. Works on the ‘‘Encapsulation of pancreatic islets aimed at insulin-dependent type 1 diabetes mellitus therapy” project under the guidance of Professor Dr. Mari Cleide Sogayar. Has experience in cell and molecular biology, genetics, and virology.
Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (T1D): Molecular Bases and Cell Therapy – Thematic Project 2016/05311-2.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic disease characterized by the absence of insulin production (DM1) or inefficiency in its use by the individual (DM2). Consequently, patients with DM develop hyperglycemia, which cantrigger serious complications in the functioning of vital organs if not controlled (DIABETES CONTROL AND COMPLICATIONS TRIALS RESEARCH GROUP – DCCT, 1993). Conventional DM1 treatments, in most cases, are not able to maintain perfect control of glycemic levels (DCCT, 1997). The surgical risks inherent to whole organ pancreas transplantation have stimulated the development of less invasive procedures in which pancreatic islets transplantations are performed. Pancreatic islet transplantation has been one of the strategies studied as cell therapy for this disease, including by our research group, which introduced this technology in Brazil (ELIASCHEWITZ et al, 2004). However, a limiting point to islet transplantation protocols for DM1 reversal is the low availability of pancreas donors and the maintenance and survival of the islets in culture after isolation. Given the growing need to search for new therapeutic interventions for DM1, strategies based on the differentiation of stem cells into insulinproducing cells have shown to be a promising approach to overcome the dependence on human pancreatic β-cells for transplantation (LOJUDICE; SOGAYAR, 2008). The in vitro differentiation process consists of consecutive steps of treatments with cytokines or signaling modulators, at specific doses, to activate or inhibit the main signaling pathways that control pancreatic organogenesis (Figures 1 and 2).
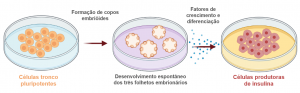
Figure 1: Differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into insulin-producing cells through the application of growth factors and differentiation that participate in pancreatic organogenesis.
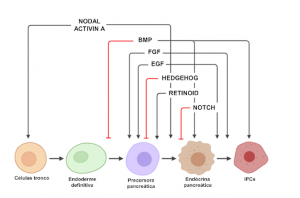
Figure 2: Schematic representation of signaling pathways that coordinate each stage of βpancreatic differentiation.
The NUCEL grouphas been seeking to establish a differentiation protocol that allows functional insulin-producing cells to be obtained in large numbers (LOJUDICE, 2008; KOSSUGE, 2013; DA SILVA, 2018). Based on the protocol established by the group, this project aims to analyze the transcriptomic profile and the role of BMP7 and PDGF-BB factors, produced in our laboratory, during the process of differentiation of murine embryonic stem cells (mESCs) into insulin-producing cells (IPCs). The exploration of the effects of these factors during in vitro differentiation is based on the mitogenic potential associated with PDGF-BB (CHEN et al., 2011) and on the ability of BMP-7 to drive the differentiation of non-endocrine progenitor cells into endocrine cells (KLEIN et al., 2015; QADIR et al., 2018), demonstrating the possibility of applying these factors in the expansion and terminal maturation of IPCs. The RNAseq transcriptome analysis of the differentiation of mESCs into IPCs will allow tracing regulatory pathways and identify the key molecules that act in the differentiation processes. Subsequently, the most relevant transcripts will be selected to carry out molecular interventions (overexpression and/or gene knockout), in a functional genomics approach. These experiments will lead to the improvement of the efficiency achieved in the in vitro differentiation protocols, and the characterization of molecules, both of which may open up new perspectives for the treatment of DM1.
REFERENCES
CHEN, H. et al. PDGF signalling controls age-dependent proliferation in pancreatic β-cells. Nature, v. 478, n. 7369, p. 349–355, 2011.
DA SILVA, C. L. L. Terapias alternativas para o diabetes mellitus tipo 1: caracterização funcional do gene Txnip na diferenciação β-pancreática e desenvolvimento de biomaterial inovados para microencapsulamento celular. 203 p. Tese (Doutorado em Ciências Biológicas (Bioquímica)) – Instituto de Química, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, 2018.
DIABETES CONTROL AND COMPLICATIONS TRIAL RESEARCH GROUP. Hypoglycemia in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes, v. 46, n. 2, p. 271-86, 1997.
DIABETES CONTROL AND COMPLICATIONS TRIAL RESEARCH GROUP. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med, v. 329, n. 14, p. 977-86, 1993.
ELIASCHEWITZ, Freddy Goldberg et al. First Brazilian pancreatic islet transplantation in a patient with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Transplantation proceedings, v. 36, n. 4, p. 1117-1118, 2004.
KLEIN, Dagmar et al. BMP-7 induces adult human pancreatic exocrine-to-endocrine conversion. Diabetes, v. 64, n. 12, p. 4123-4134, 2015.
KOSSUGUE, P. M. Diferenciação de células-tronco embrionárias murinas (mESCs) em células produtoras de insulina (IPCs) e caracterização funcional do gene Purkinje Cell Protein 4 (Pcp4) neste processo. Tese (Doutorado em Ciências (Bioquímica) – Instituto de Química, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, 2013.
LOJUDICE, F. H. Identificação de genes diferencialmente expressos durante diferenciação de células-tronco e caracterização de células progenitoras mesenquimais. 173 p. Tese (Doutorado em Ciências Biológicas (Bioquímica)) – Instituto de Química, Universidade de São Paulo, 2008.
LOJUDICE, Fernando Henrique; SOGAYAR, Mari Cleide. Células-tronco no tratamento e cura do diabetes mellitus. Ciência & Saúde Coletiva, v. 13, p. 19-21, 2008.
QADIR, M. M. F. et al. P2RY1/ALK3-expressing cells within the adult human exocrine pancreas are BMP-7 expandable and exhibit progenitor-like characteristics. Cell reports, v. 22, n. 9, p. 2408-2420, 2018.

